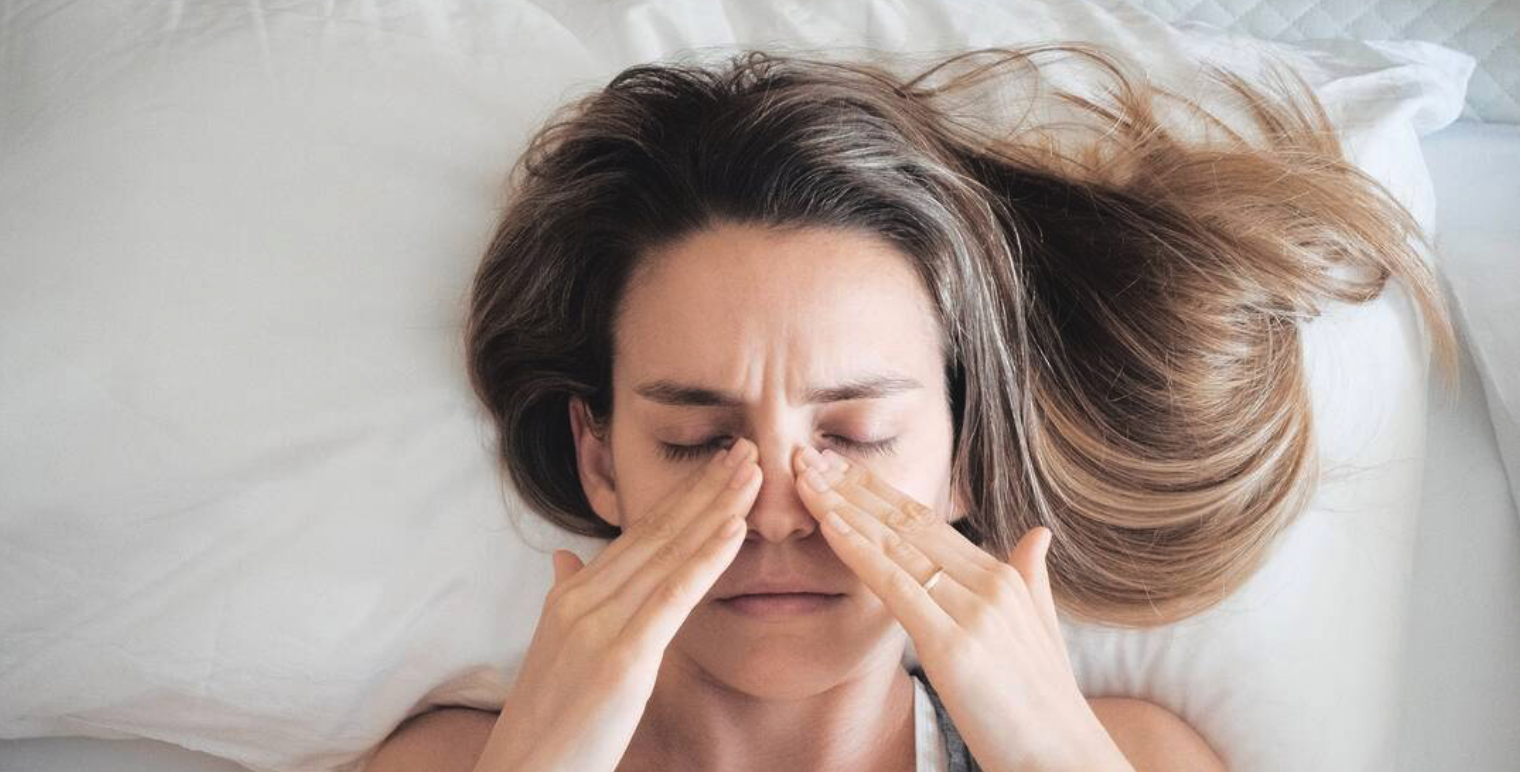
Unknown to the general public and yet as common as intolerance to FODMAPs and gluten, histamine intolerance can be the cause of manifestations encountered in everyday life: migraines, digestive disorders, muscle pain, fatigue, skin problems, dizziness, brain fog, insomnia, night sweats, vertigo, hypersensitivity to chemical noises and smells, etc….
Histamine intolerance is the consequence of a too high concentration of histamine in the body, which results in an imbalance between its accumulation and the body’s ability to degrade it.
What is histamine?
Naturally present in the body as well as in many everyday foods, histamine is a molecule widely involved in the pathophysiology of many inflammatory and allergic phenomena (food intolerance, atopy, etc.). However, at low doses, it helps to regulate a wide variety of physiological processes such as gastric acid secretion, neurotransmission, immune defense or microcirculation. Histamine, which has useful pharmacological properties, can also be certain toxic to the body.
Histamine degradation
Histamine is degraded by two enzymes, HNMT and DAO. The first acts in the nervous system, while diamine oxidase (DAO) acts in the intestine. This enzyme allows us to eat foods that contain histamine without the symptoms accompanying its release. Histamine intolerance may be related to the fact that this enzyme is not operational. Its proper functioning is conditioned by correct levels of vitamin B6 and B12, zinc, iron, and also vitamin C.
An organism deficient in vitamins and minerals may develop an exacerbated sensitivity to foods containing histamine.
Other factors to consider
Certain foods have the property of inactivating or inhibiting DAO, such as alcohol, energy drinks and tea.
In case of intestinal hyperpermeability / alteration of the intestinal mucosa, the production of DAO will be disturbed.
Dysbiosis, and more particularly candidiasis, can also disrupt the degradation of histamine, as well as Sibo (small intestine bacterial infection).
Foods and histamines
High Histamine Foods Alcohol, aged cheeses, charcuterie, smoked and marinated fish, canned fish, sauerkraut, vegetables marinated in vinegar, olives, dairy products, dried fruits, aubergine, spinach, processed or smoked meat, shellfish, fermented or pickled foods, vinegar.
Histamine Releasers These foods are low in histamines but can trigger the release of histamine and create problems for people with histamine intolerance: Avocados, bananas, citrus fruits (kiwi, lemon, lime), strawberries, tomatoes (especially ketchup and tomato juice).
Diamine Oxidase (DAO) Blockers These foods block DAO – the enzyme that controls histamine and should be avoided: Alcohol, energy drinks, teas (black & green).
How I can help
NAET/Total Reset®+ naturopathy support
The NAET/Total Reset® method is very useful for identifying the sources of histamine sensitivity, and for correcting imbalances.
A dietary rebalancing may be necessary before the basic work of the method is sufficiently advanced.
It will also be crucial to work on stress and emotional management, which are very involved.
Finally, some patients will greatly benefit from supplementation. Approximately 15% of the population suffer from histamine intolerance, with a higher prevalence in women. However, natural solutions can be provided to limit this phenomenon, in particular through the provision of natural DAO and active ingredients that promote the degradation of histamine.
If you suspect a histamine intolerance, I invite you to make an appointment for a consultation which will test the elements mentioned above.
The NAET/Total Reset@ method rectifies and reinforces the ground of the person in its foundations, in order to allow the attenuation then the disappearance of the symptoms, step by step.
To book a session with me, call Clinica Alostase +351 934 363 040